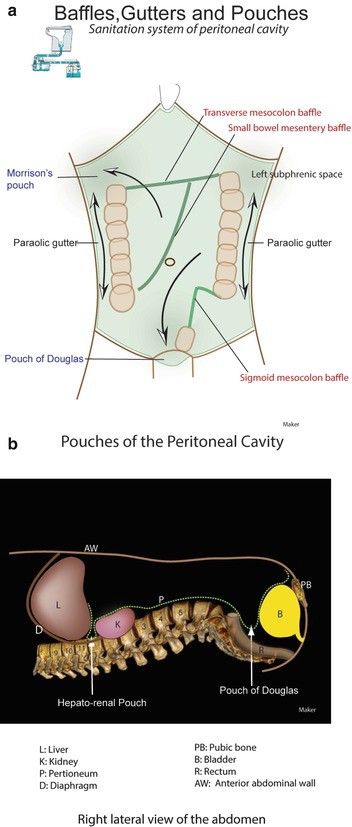
As the left paracolic gutter is shallow and discontinuous with left subdiaphragmatic space at the phrenicocolic ligament most of the fluid takes path through the right paracolic gutter.
Left paracolic gutter nodule.
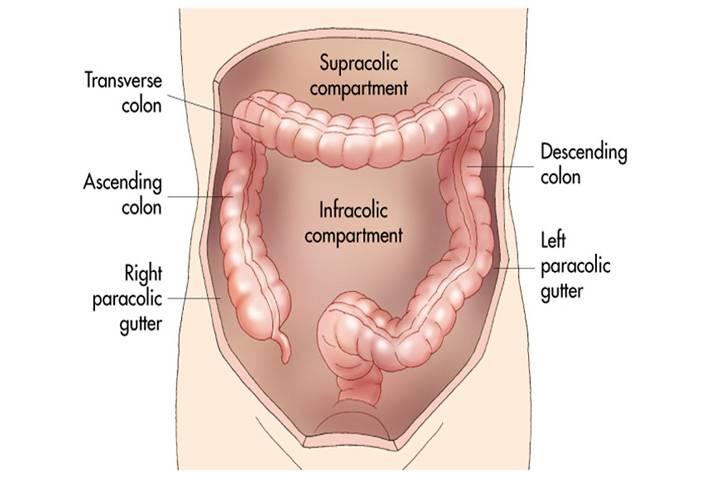
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
Consequently the majority of fluid flows into the right paracolic gutter.
The right paracolic gutter is continuous with the perisplenic space or area around the spleen.
Most of the fluid ascends via the right paracolic gutter into the right subdiaphragmatic space because the left paracolic gutter is shallow and discontinuous with the left subdiaphragmatic space at the phrenicocolic ligament and because direct passage from the right to left subdiaphragmatic space is prevented by the falciform ligament fig 1b 3 5.
Similar to its right counterpart the paracolic gutter originates from the left hepatic flexure or the meet point of the transverse and descending colon and runs downward to empty into the pelvic region or abdominal wall.
Completion of the circulatory pathway takes place caudally by redirection of fluid into the pelvis through the inframesocolic compartment13 fig.
Paracolic gutters refer to open areas between the wall of the abdomen and the colon.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon possesses a short mesentery for part of its length.
The left medial paracolic gutter.
The left paracolic gutter is shallow and is limited superiorly by the phrenicocolic ligament which extends from the splenic flexure of the colon to the diaphragm 10.